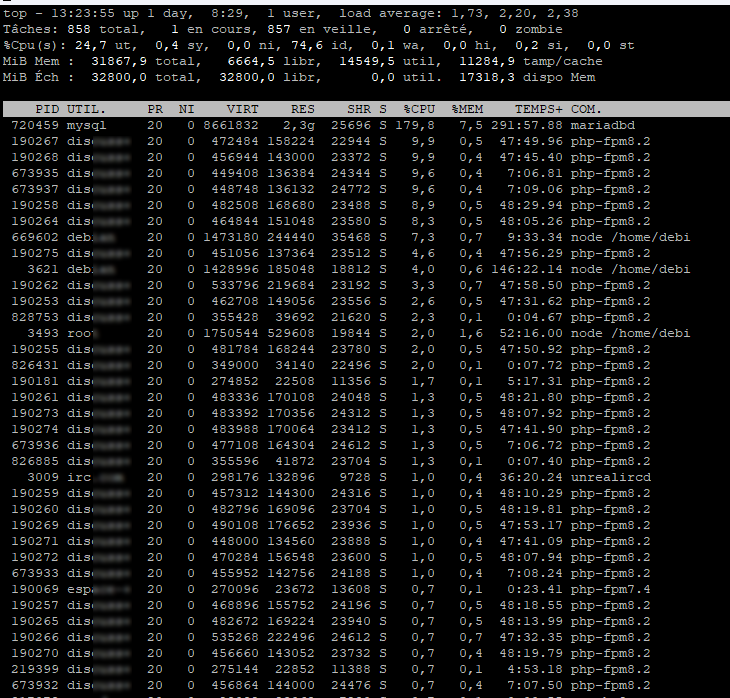
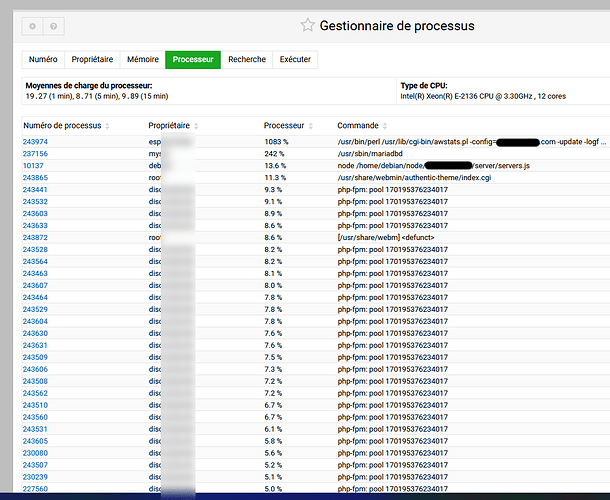
Here are the current statuses (I haven’t changed anything yet):
MPM is a prefork
debian@ns:~$ sudo apachectl -V | grep MPM
Server MPM: prefork
debian@ns:~$
KeepAlive is off
MaxKeepAliveRequests is 500
KeepAliveTimeout is 5
PHP FPM is enabled on all sites
Opcache does not appear to be enabled
Regarding cron jobs, there aren’t many, except for numerous lines like this:
/etc/webmin/virtualmin-awstats/awstats.pl thesite.com
There are 45 of these, but there could be 10 more that I haven’t counted. Maybe it would be better to disable Awstats since I don’t use it?!
If I ignore all the Awstats entries, there are barely 10 to 15 cron jobs left, and to me, it doesn’t seem to be a problem, except for all the Awstats entries.
About Swap! Oh yes, I remember back in December 2023, I had issues with it initially, before putting the dedicated server into production. I had to reinstall the server twice because the swap was incorrectly set in the partition, only 500MB, and then I was advised to disable the swap. However, it was set to a new value, which I don’t know. I followed this tutorial: Swappiness ou comment utiliser au maximum sa Ram | Linux et Geekeries and the swappiness was set to 0. I was recommended to disable it, but should I have? I have a total of 32GB of memory on the dedicated server. I don’t remember the partition’s “swap” size, I have no idea. I’m really not knowledgeable about Swap.
Here is the current memory status: Real memory: 18.67GB used / 7.92GB cached / 31.12GB total
There are about 40 sites in total, not counting the subdomains, which could bring the total to 80 sites.
There are between 13,000 and 20,000 visitors spread across all sites each day.
Here is the configuration of MariaDB:
# The MariaDB configuration file
#
# The MariaDB/MySQL tools read configuration files in the following order:
# 0. "/etc/mysql/my.cnf" symlinks to this file, reason why all the rest is read.
# 1. "/etc/mysql/mariadb.cnf" (this file) to set global defaults,
# 2. "/etc/mysql/conf.d/*.cnf" to set global options.
# 3. "/etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/*.cnf" to set MariaDB-only options.
# 4. "~/.my.cnf" to set user-specific options.
#
# If the same option is defined multiple times, the last one will apply.
#
# One can use all long options that the program supports.
# Run program with --help to get a list of available options and with
# --print-defaults to see which it would actually understand and use.
#
# If you are new to MariaDB, check out https://mariadb.com/kb/en/basic-mariadb-articles/
#
# This group is read both by the client and the server
# use it for options that affect everything
#
[client-server]
# Port or socket location where to connect
# port = 3306
socket = /run/mysqld/mysqld.sock
# Import all .cnf files from configuration directory
#!includedir /etc/mysql/conf.d/
#!includedir /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/
[mysqld]
#user = root
max_allowed_packet = 1024M
max_connect_errors = 1000000
performance-schema=0
default-storage-engine=InnoDB
# === InnoDB Settings ===
#default_storage_engine = InnoDB
#innodb_buffer_pool_instances = 4 # Use 1 instance per 1GB of InnoDB pool size - max is 64
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 4G # Use up to 70-80% of RAM
innodb_file_per_table = 1
innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit = 0
innodb_flush_method = O_DIRECT
innodb_log_buffer_size = 16M
innodb_log_file_size = 1G
innodb_sort_buffer_size = 4M # UPD - Defines how much data is read into memory for sorting operations before writing to disk (default is 1M / max is 64M)
innodb_stats_on_metadata = 0
#innodb_use_fdatasync = 1 # Only (!) for MySQL v8.0.26+
#innodb_temp_data_file_path = ibtmp1:64M:autoextend:max:20G # Control the maximum size for the ibtmp1 file
#innodb_thread_concurrency = 4 # Optional: Set to the number of CPUs on your system (minus 1 or 2) to better
# contain CPU usage. E.g. if your system has 8 CPUs, try 6 or 7 and check
# the overall load produced by MySQL/MariaDB.
innodb_read_io_threads = 64
innodb_write_io_threads = 64
#innodb_io_capacity = 2000 # Depends on the storage tech - use 2000 for SSD, more for NVMe
#innodb_io_capacity_max = 4000 # Usually double the value of innodb_io_capacity
# === MyISAM Settings ===
# The following 3 options are ONLY supported by MariaDB & up to MySQL 5.7
# Do NOT un-comment on MySQL 8.x+
#query_cache_limit = 4M # UPD
#query_cache_size = 64M # UPD
#query_cache_type = 1 # Enabled by default
key_buffer_size = 24M # UPD
low_priority_updates = 1
concurrent_insert = 2
# === Connection Settings ===
max_connections = 1000 # UPD - Important: high no. of connections = high RAM consumption
back_log = 512
thread_cache_size = 100
thread_stack = 192K
interactive_timeout = 180
wait_timeout = 180
# For MySQL 5.7+ only (disabled by default)
#max_execution_time = 90000 # Set a timeout limit for SELECT statements (value in milliseconds).
# This option may be useful to address aggressive crawling on large sites,
# but it can also cause issues (e.g. with backups). So use with extreme caution and test!
# More info at: https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/server-system-variables.html#sysvar_max_execution_time
# For MariaDB 10.1.1+ only (disabled by default)
#max_statement_time = 90 # The equivalent of "max_execution_time" in MySQL 5.7+ (set above)
# The variable is of type double, thus you can use subsecond timeout.
# For example you can use value 0.01 for 10 milliseconds timeout.
# More info at: https://mariadb.com/kb/en/aborting-statements/
# === Buffer Settings ===
# Handy tip for managing your database's RAM usage:
# The following values should be treated carefully as they are added together and then multiplied by your "max_connections" value.
# Other options will also add up to RAM consumption (e.g. tmp_table_size). So don't go switching your "join_buffer_size" to 1G, it's harmful & inefficient.
# Use one of the database diagnostics tools mentioned at the top of this file to count your database's potential total RAM usage, so you know if you are within
# reasonable limits. Remember that other services will require enough RAM to operate properly (like Apache or PHP-FPM), so set your limits wisely.
join_buffer_size = 4M # UPD
read_buffer_size = 3M # UPD
read_rnd_buffer_size = 4M # UPD
sort_buffer_size = 4M # UPD
# === Table Settings ===
# In systemd managed systems like Ubuntu 16.04+ or CentOS 7+, you need to perform an extra action for table_open_cache & open_files_limit
# to be overriden (also see comment next to open_files_limit).
# E.g. for MySQL 5.7, please check: https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/using-systemd.html
# and for MariaDB check: https://mariadb.com/kb/en/library/systemd/
table_definition_cache = 40000 # UPD
table_open_cache = 40000 # UPD
open_files_limit = 60000 # UPD - This can be 2x to 3x the table_open_cache value or match the system's, or 60000
# open files limit usually set in /etc/sysctl.conf and /etc/security/limits.conf
# In systemd managed systems this limit must also be set in:
# - /etc/systemd/system/mysql.service.d/override.conf (for MySQL 5.7+ in Ubuntu) or
# - /etc/systemd/system/mysqld.service.d/override.conf (for MySQL 5.7+ in CentOS) or
# - /etc/systemd/system/mariadb.service.d/override.conf (for MariaDB)
# otherwise changing open_files_limit will have no effect.
#
# To edit the right file execute:
# $ systemctl edit mysql (or mysqld or mariadb)
# and set "LimitNOFILE=" to something like 100000 or more (depending on your system limits for MySQL)
# or use "LimitNOFILE=infinity" for MariaDB only.
# Finally merge the changes with:
# $ systemctl daemon-reload; systemctl restart mysql (or mysqld or mariadb)
max_heap_table_size = 256M # Increase to 256M or 512M if you have lots of temporary tables because of missing indices in JOINs
tmp_table_size = 256M # Use same value as max_heap_table_size
# === Search Settings ===
ft_min_word_len = 3 # Minimum length of words to be indexed for search results
# === Binary Logging ===
disable_log_bin = 1 # Binary logging disabled by default
#log_bin # To enable binary logging, uncomment this line & only one of the following 2 lines
# that corresponds to your actual MySQL/MariaDB version.
# Remember to comment out the line with "disable_log_bin".
#expire_logs_days = 1 # Keep logs for 1 day - For MySQL 5.x & MariaDB before 10.6 only
#binlog_expire_logs_seconds = 86400 # Keep logs for 1 day (in seconds) - For MySQL 8+ & MariaDB 10.6+ only
event_scheduler=1
# fin
# === SQL Compatibility Mode ===
# Enable for b/c with databases created in older MySQL/MariaDB versions
# (e.g. when using null dates)
#sql_mode = ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION,ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES
# Crappy SQL queries/schema? Go bold!
sql_mode=""
local-infile=1
# === Error & Slow Query Logging ===
log_error = /var/log/mariadb/mysql_error.log
log_queries_not_using_indexes = 0 # Disabled on production
long_query_time = 5
slow_query_log = 0 # Disabled on production
slow_query_log_file = /var/log/mariadb/mysql-slow.log
#general_log = 1
#general_log_file = /var/log/mariadb/mysql.log
[mysqldump]
# Variable reference
# For MySQL 5.7+: https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/mysqldump.html
# For MariaDB: https://mariadb.com/kb/en/library/mysqldump/
quick
quote_names
max_allowed_packet = 1024M
For Apache, should I apply everything you mentioned, or are there any new ideas based on the information I’ve provided?